Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU)
Elliot Hospital offers the only Level III Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU) in southern New Hampshire. Our team of neonatal experts care for preterm infants as early as 23-weeks gestation.
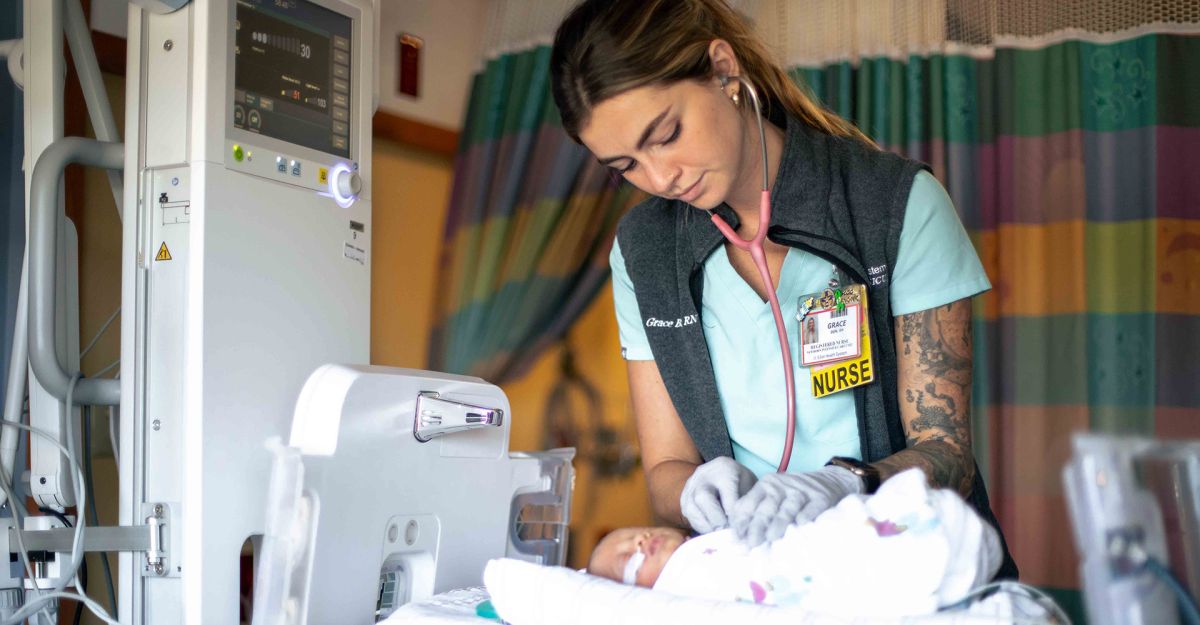

Elliot Hospital offers the only Level III Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU) in southern New Hampshire. Our team of neonatal experts care for preterm infants as early as 23-weeks gestation.
Recognized regionally for top-quality care since 1989, The Elliot’s Level III NICU has touched the lives of thousands of families across our region and beyond. Few parents anticipate their newborns needing intensive care. But when there is no time for doubt, you can count on our skilled team to ensure your baby receives expert care provided in a nurturing, family-oriented setting that's conveniently located close to home.
Our Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU) operates around the clock, equipped with cutting-edge technology and staffed by a dedicated team. With 34 beds, or isolettes, available, we provide specialized care for over 600 critically ill and premature infants annually, ensuring a nurturing environment tailored to each baby's unique requirements.
 Elliot Health System is pleased to announce that U.S. News and World Report has ranked Elliot Hospital’s maternity services as high performing in its 2025 Best Hospitals for Maternity Care awards.
Elliot Health System is pleased to announce that U.S. News and World Report has ranked Elliot Hospital’s maternity services as high performing in its 2025 Best Hospitals for Maternity Care awards.
U.S. News and World Report evaluates how well hospitals perform in childbirth using several indicators. The high performing rating indicates that Elliot Hospital is well above average on a range of objective quality measures, such as rates of unexpected complications, C-sections, and breast milk feeding rates.
At The Elliot’s NICU, our multidisciplinary team works collaboratively to ensure each infant receives optimal care tailored to their unique needs. Our dedicated team is committed to providing compassionate, family-centered care while leveraging their expertise to promote the health and well-being of every infant in our care. Your baby will benefit from the expertise of a diverse range of specialists, including:
Experts in the care of newborns, specializing in premature and critically ill infants.
Trained in surgical procedures specific to infants and children.
Specialists in administering anesthesia to infants and children undergoing surgery or other medical procedures.
Focused on diagnosing and treating gastrointestinal conditions in infants and children.
Specializing in the diagnosis and treatment of neurological disorders affecting newborns.
Assist in providing primary and specialized care under the guidance of neonatologists.
Specialized in diagnosing and treating eye conditions in infants.
Experts in interpreting imaging studies to aid in diagnosis and treatment planning.
Ensure that infants receive appropriate nutrition for optimal growth and development.
Manage medication therapies to ensure safe and effective treatment for infants.
Help infants develop motor skills and address any physical or developmental challenges.
Assist mothers with breastfeeding support and guidance.
Understanding levels of neonatal care, as determined by the American Academy of Pediatrics, can guide decisions about where to seek care and what parents can expect for their baby.
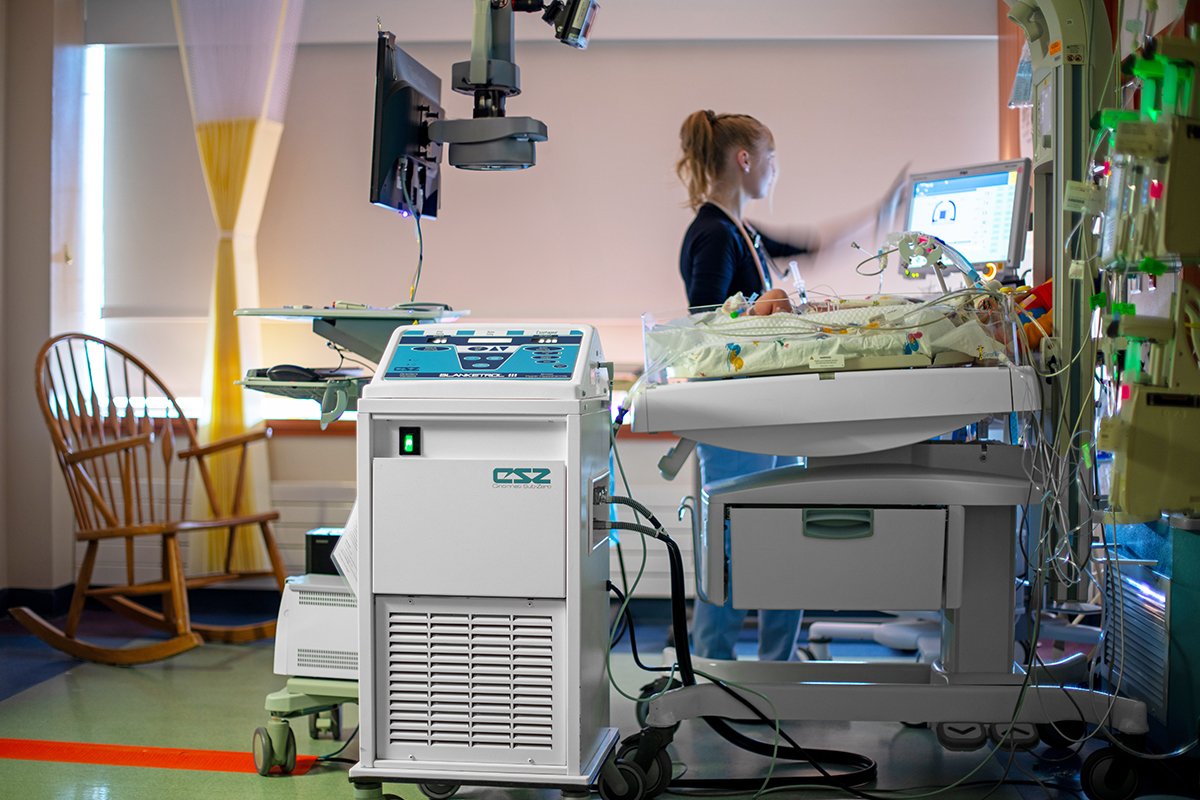
With a focus on early intervention, our interdisciplinary team blends medical proficiency, compassion, and state-of-the-art equipment to support both infants and their families.
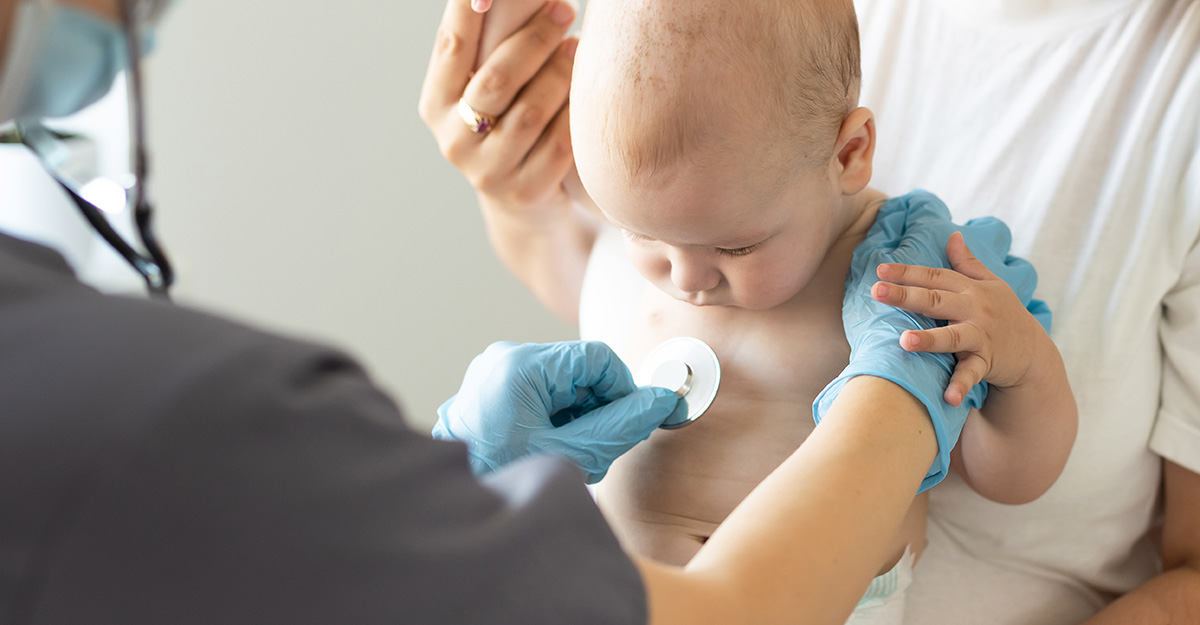
Our NICU Follow-up Clinic has a powerful impact on the development of our NICU graduates. Over the critical first two years of life, qualifying infants receive dedicated care from our expert multidisciplinary team after they leave our facility. Led by expert neonatologists, alongside nutritionists and occupational or physical therapists, we ensure holistic support. Our team conducts comprehensive developmental neurological, nutritional, and medical assessments tailored to each infant's unique needs. We collaborate closely with primary care pediatricians and families, facilitating seamless integration of supportive services when needed.
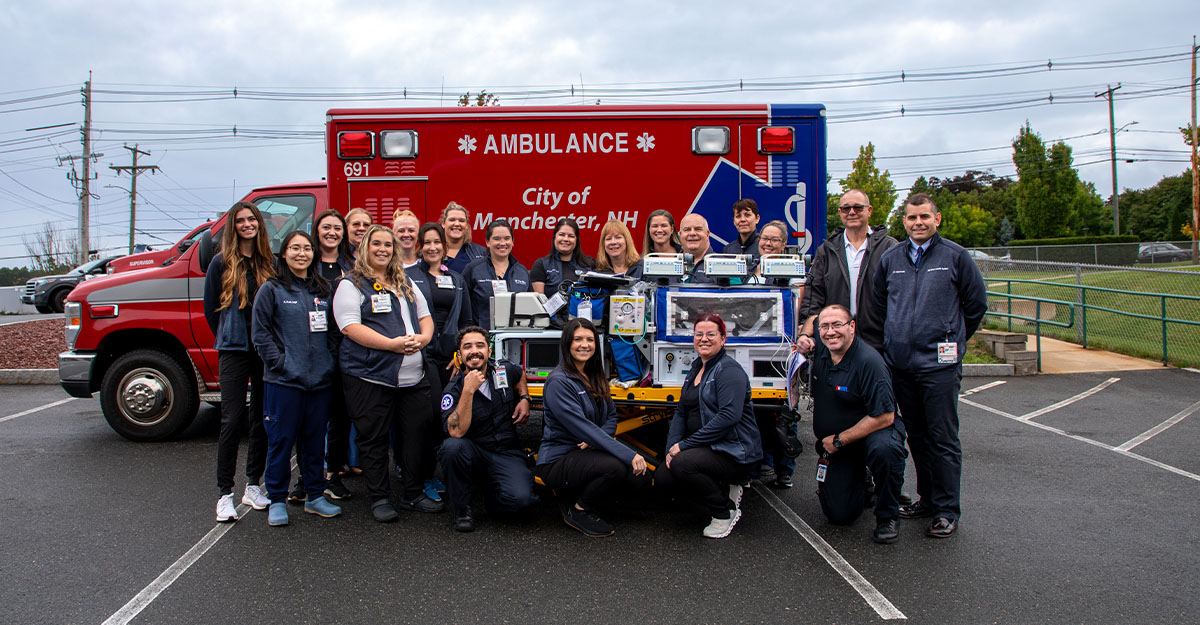

Elliot Hospital's specialized NICU transport team is also available to bring babies born at other regional hospitals to The Elliot for advanced care. Expert care begins during transport - the team includes a licensed advanced practice provider as well as a specialized neonatal registered nurse, skilled respiratory therapist, and emergency medical technicians working seamlessly to begin care before your infant reaches our doors.

We pride ourselves on providing family-centered care. At our NICU, parents are active care team partners, invited to join daily rounds with their infant alongside our multidisciplinary experts. We believe in open communication and collaboration, regularly checking in with parents to discuss care plans and address any questions or concerns they may have.
In addition, our NICU Family Community Group convenes weekly, providing a supportive space for parents to connect, share experiences, and learn from our dedicated team of NICU nurses, occupational and physical therapists, and providers. Together, we foster a community of strength, resilience, and mutual support.

We partner with three Manchester-area-based OB/GYN practices for labor and delivery at Elliot Hospital. These practices collaborate with our NICU team when needed and have a long history of delivering babies at Elliot Hospital.
From pediatricians focused on family-centered care to specialists who perform intricate pediatric surgical procedures, Elliot Hospital offers all of the pediatric services you need close to home.
Learn More
As the only birthing center in the area with a full suite of labor and delivery rooms and postpartum rooms to support your recovery, we have the expertise and flexibility to manage all your birthing needs in one location. Lactation support is available whenever needed, and our team is committed to supporting parents throughout their birthing experience.
Learn More